Simple Past
O Simple Past , também chamado de Past Simple (passado simples), é um dos tempos verbais do inglês. Ele é equivalente ao passado simples na língua portuguesa.
Quando usar?
O Simple Past é usado para indicar ações passadas já concluídas, ou seja, para falar de fatos que já aconteceram; que começaram e terminaram no passado.
Expressões temporais usadas com o Simple Past
Para reforçar o uso do Simple Past, muitas expressões temporais são utilizadas nas frases.
Os exemplos mais usuais são: yesterday (ontem), the day before yesterday (anteontem), last night (ontem à noite), last year (ano passado), last month (mês passado), last week (semana passada), ago (atrás), etc.
Veja algumas frases no Simple Past com as expressões acima:
- We did not go to school yesterday. (Nós não fomos para a escola ontem.)
- His birthday was the day before yesterday. (O aniversário dele foi anteontem.)
- She studied Math last night. (Ela estudou matemática ontem à noite.)
- I traveled1/ travelled2 to Brazil last year. (Eu viajei para o Brasil ano passado.)
- They visited their uncle last month. (Eles visitaram o tio deles mês passado.)
- I called you three days ago. (Eu telefonei para você três dias atrás.)
- We learned how to dance samba last week. (Nós aprendemos a dançar samba semana passada.)
1 grafia americana; 2 grafia britânica
Formação do Simple Past
A formação básica do Simple Past é feita com o uso do auxiliar did nas formas negativa e interrogativa, e com o acréscimo de –ed, –ied ou –d ao final do verbo principal no infinitivo, sem o to, na forma afirmativa.
Observe as tabelas abaixo e confira exemplos de conjugação do Simple Past.
Exemplo: verbo to dance (dançar - regular)
| Affirmative | Negative | Interrogative |
|---|---|---|
| I danced | I did not dance | Did I dance? |
| You danced | You did not dance | Did you dance? |
| He danced | He did not dance | Did he dance? |
| She danced | She did not dance | Did she dance? |
| It danced | It did not dance | Did it dance? |
| We danced | We did not dance | Did we dance? |
| You danced | You did not dance | Did you dance? |
| They danced | They did not dance | Did they dance? |
Exemplo: verbo to fly (voar - irregular)
| Affirmative | Negative | Interrogative |
|---|---|---|
| I flew | I did not fly | Did I fly? |
| You flew | You did not fly | Did you fly? |
| He flew | He did not fly | Did he fly? |
| She flew | She did not fly | Did she fly? |
| It flew | It did not fly | Did it fly? |
| We flew | We did not fly | Did we fly? |
| You flew | You did not fly | Did you fly? |
| They flew | They did not fly | Did they fly? |
Confira as explicações abaixo e aprenda como escrever frases com verbos no passado em inglês na forma afirmativa, na forma negativa e na forma interrogativa.
Affirmative form (forma afirmativa)
Regular verbs (verbos regulares)
Para usar os verbos regulares em frases afirmativas no Simple Past, basta mudar a terminação do verbo de acordo com as seguintes regras:
1. Aos verbos regulares terminados em –e, acrescenta-se somente o –d no final do verbo:
- to love (amar) – loved
- to lie (mentir) – lied
- to arrive (chegar) – arrived
- to like (gostar) – liked
2. Aos verbos regulares terminados em consoante+vogal+consoante (CVC), duplica-se a última consoante e acrescenta-se o –ed:
- stop (parar) – stopped
- control (controlar) – controlled
- plan (planejar) – planned
- prefer (prefer) – preferred
3. Aos verbos terminados em –y precedido de consoante, retira-se o y e acrescenta-se o –ied:
- to study (estudar) – studied
- to worry (preocupar-se) – worried
- to cry (chorar) – cried
- to try (tentar) – tried
4. Aos verbos terminados em –y precedido de vogal, acrescenta-se somente o –ed:
- enjoy (aproveitar) – enjoyed
- stay (ficar) – stayed
- play (brincar; jogar) – played
Irregular verbs (verbos irregulares)
Os verbos irregulares não possuem um padrão de formação. Eles não seguem as regras indicadas acima pois possuem uma forma própria.
Confira abaixo alguns verbos irregulares no passado simples:
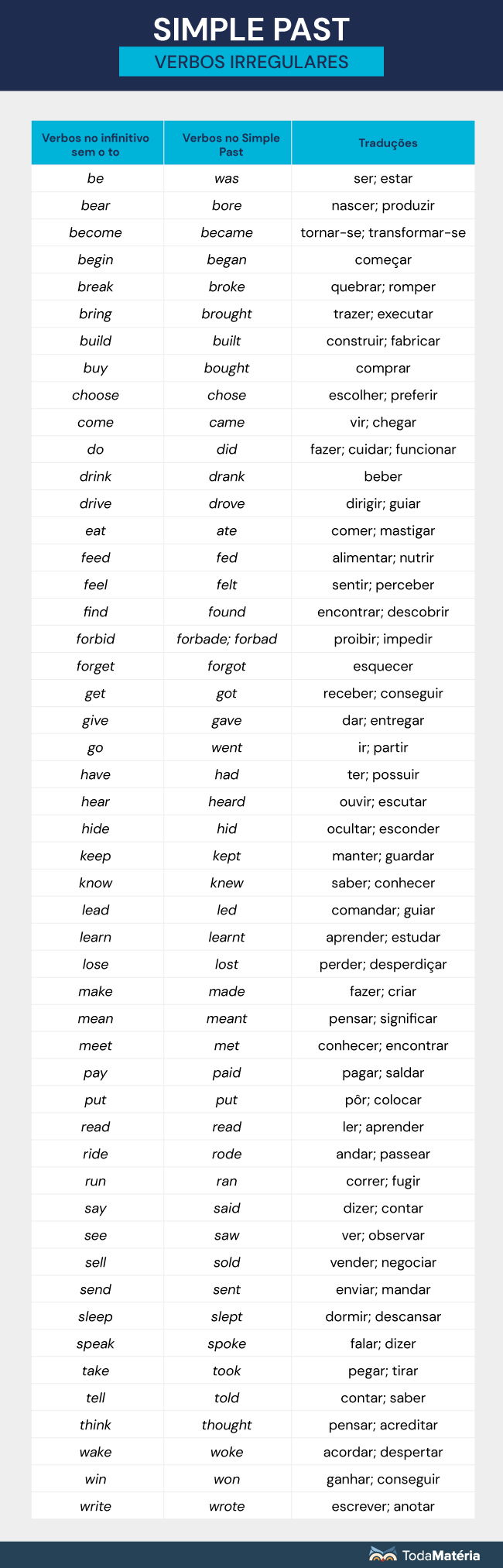
A formação de frases na afirmativa no Simple Past segue a estrutura abaixo:
Sujeito + verbo + complemento
Exemplo: She liked the English teacher. (Ela gostou da professora de inglês).
Negative Form (Forma Negativa)
Para a construção de frases negativas no Simple Past, o verbo did é empregado como verbo auxiliar.
O verbo principal não é conjugado no passado, uma vez que o auxiliar já indica o tempo verbal.
Sua estrutura frasal é feita da seguinte forma:
Sujeito + did + not + verbo principal + complemento
Exemplo: She did not like the English teacher. (Ela não gostou da professora de inglês)
Obs.: a forma contraída de did not é didn’t.
Interrogative Form (Forma Interrogativa)
Da mesma maneira que acontece na forma negativa, o did é o verbo auxiliar utilizado para as frases interrogativas no Simple Past .
Veja a estrutura abaixo:
Did + sujeito + verbo principal + complemento
Exemplo: Did she like the English teacher? (Ela gostou da professora de inglês?)
Obs.: somente o verbo auxiliar (did) é conjugado no Simple Past. Não é necessário conjugar o verbo principal.
Simple Past x Past Continuous
Muitos confundem os usos do passado em inglês, sobretudo do Simple Past (passado simples) e do Past Continuous (passado contínuo). Vejamos abaixo as diferenças entre eles:
Simple Past
Expressa ações passadas, ou seja, refere-se a fatos que começaram no passado e terminaram no passado. Nesse caso, as ações já foram concluídas. O verbo auxiliar did é usado somente nas formas negativa e interrogativa do Simple Past.
Exemplos:
- You ran in the marathon. (Você correu na maratona.)
- You did not run in the marathon. (Você não correu na maratona.)
- Did you run in the marathon? (Você correu na maratona?)
Past Continuous
Expressa uma ação contínua que ocorreu no passado.
Diferentemente do Simple Past, ele é formado pelo verbo auxilar to be conjugado no Simple Past (was/were) + o gerúndio (-ing) do verbo principal.
Exemplos:
- You were running in the marathon. (Você estava correndo na maratona.)
- You were not running in the marathon. (Você não estava correndo na maratona.)
- Were you running in the marathon? (Você estava correndo na maratona?)
Vídeo sobre Simple Past
No vídeo abaixo você encontra um resumo sobre o uso do Simple Past e dicas valiosas que vão ajudá-lo a usar esse tempo verbal corretamente.
Exercises (Exercícios)
1. (PUC-GO) Complete the following text using the correct past tense conjugation of the verbs in parenthesis in English:
Last night Susan (go) ____________ to her friend’s birthday party. She (dance) ____________ with her boyfriend, and (eat) ____________ cake. After they (leave) ____________ the party, Susan and her boyfriend (decide) ____________ to go and watch a movie at the theater. They (see) ____________ the new Transformer’s movie, and then they went home. When she (get) ____________ home, Susan (take) ____________ a shower and (fall) ____________ asleep quickly.
Choose the correct option from the ones listed below:
a) go/ dance / eat / leave / decide / see / get / take / fall.
b) went / danced / ate / left / decided / saw / got / took / fell.
c) will go / will dance / will eat / will leave / will decide / will see / will get / will take / will fall.
d) had gone / had danced / had eaten / had left / had decided / had seen / had gotten / had taken / had fallen.
2. (Mackenzie) The negative form of He sold his car last week is:
a) He doesn’t sells his car last week.
b) He doesn’t sold his car last week.
c) He didn’t sold his car last week.
d) He didn’t sell his car last week.
e) He doesn’t sell his car last week
3. Complete as lacunas com os verbos entre parênteses conjugados no Simple Past:
a) She _______(go) to the shopping mall.
b) Marisa _______ (want/not) a ride.
c) Your parents _______ (make) a cake.
d) ______ (you talk) to his friends?
e) Sofia and Jane _______ (be) at the party.
4. Assinale a alternativa correta para o Simple Past dos verbos irregulares: drive, forget e got.
a) drive; forgot; got
b) driven; forgotten; get
c) driven; forgotten; gotten
d) drove; forget; get
e) drove; forgot; got
5. Escreva a frase abaixo no Simple Past, nas formas afirmativa, negativa e interrogativa:
She will go to the United States of America.
Quer saber mais sobre os verbos em inglês? Não deixe de ler os conteúdos abaixo:
- Verbos regulares e irregulares em inglês (exercícios)
- Simple Past (exercícios com gabarito comentado) - nível médio
- Exercícios sobre Past Continuous com gabarito comentado
- Was e were: formas afirmativa, negativa e interrogativa
MUNIZ, Carla. Simple Past. Toda Matéria, [s.d.]. Disponível em: https://www.todamateria.com.br/simple-past/. Acesso em:



